 We know more than anyone the importance of a healthy spine. Your spinal cord is a huge player in how you feel and function as a whole; there’s a reason why it’s one of the few organs in your body encased in armor.
We know more than anyone the importance of a healthy spine. Your spinal cord is a huge player in how you feel and function as a whole; there’s a reason why it’s one of the few organs in your body encased in armor.
And this armor, the spine, is made up of 33 individual vertebrae that are divided into three sections—the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spines.
Starting from the top, literally, with your cervical spine; let’s shine a light on the importance and what role the cervical spine plays in overall function.
The Importance of Your Cervical Spine
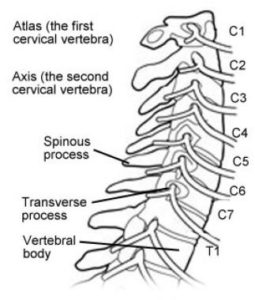
Your cervical spine—the first seven vertebrae at the top of the spine—is located in the neck. It has the important job of supporting the head, enabling its flexibility and facilitating blood flow to the brain. It houses and protects the top section of the spinal cord, playing a crucial role in the function of your central nervous system.
When Your Cervical Spine is Misaligned
The positioning of your vertebrae can be affected by stressors both big and small, like physical traumas from accidents to small repetitions like posture and staring at a computer screen all day. These factors have the power to knock vertebrae out of alignment, a condition known as a subluxation. Subluxated vertebrae put pressure on the spinal nerves, effectively muting communication from the brain to other organs in the body, leaving them vulnerable.
Take a look at each vertebra and how it connects with different organs and areas in the body. And most importantly, identify any possible symptoms that could arise from a subluxation in that vertebra!
Cervical Region aka the neck
Vertebrae & Parts of the Body & Possible Symptoms
C1 Blood supply to the head, pituitary gland, scalp, bones of the face, brain, inner and middle ear,
sympathetic nervous system. Headaches, nervousness, insomnia, head colds, high blood pressure, migraines, anxiety, amnesia, chronic tiredness and dizziness.
C2 Eyes, optic nerves, auditory nerves, sinuses,
mastoid bones, tongue and forehead. Sinus trouble, allergies, pain around the
eyes, earaches and fainting spells.
C3 Cheeks, outer ear, face bones, teeth and facial nerve. Neuralgia, neuritis, acne and eczema.
C4 Nose, lips, mouth and Eustachian tube. Hay fever, runny nose and hearing loss.
C5 Vocal cords, neck glands and pharynx. Laryngitis, hoarseness & throat conditions.
C6 Neck muscles, shoulders, tonsils. Stiff neck, upper arm pain, tonsillitis,
chronic cough and croup.
C7 Thyroid gland, bursa in the shoulders, elbows. Bursitis, colds and thyroid conditions.



Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.